Population EcologyPage
7
7
Zero population growth = High birth rate – High death rate
Zero population growth = Low birth rate – Low death rate
The demographic transition is the move from the first state toward the second state.
Slide 45
Age Structure
One important demographic factor in present and future growth trends is a country’s age structure.
Age structure is the relative number of individuals at each age.
Age structure diagrams can predict a population’s growth trends.
They can illuminate social conditions and help us plan for the future.
Slide 46
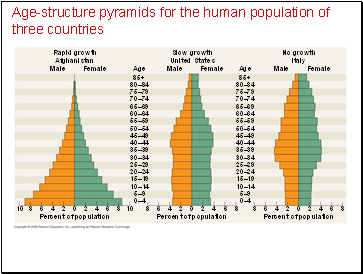
Age-structure pyramids for the human population of three countries
Rapid growth
Afghanistan
Male
Female
Age
Age
Male
Female
Slow growth
United States
Male
Female
No growth
Italy
85+
80–84
75–79
70–74
60–64
65–69
55–59
50–54
45–49
40–44
35–39
30–34
25–29
20–24
15–19
0–4
5–9
10–14
85+
80–84
75–79
70–74
60–64
65–69
55–59
50–54
45–49
40–44
35–39
30–34
25–29
20–24
15–19
0–4
5–9
10–14
10
10
8
8
6
6
4
4
2
2
0
Percent of population
Percent of population
Percent of population
6
6
4
4
2
2
0
8
8
6
6
4
4
2
2
0
8
8
Slide 47
Estimates of Earth’s Carrying Capacity
How many humans can the biosphere support?
The carrying capacity of Earth for humans is uncertain.
The average estimate is 10–15 billion.
Slide 48
Limits on Human Population Size
The ecological footprint concept summarizes the aggregate land and water area needed to sustain the people of a nation.
It is one measure of how close we are to the carrying capacity of Earth.
Countries vary greatly in footprint size and available ecological capacity.
Our carrying capacity could potentially be limited by food, space, nonrenewable resources, or buildup of wastes.
Slide 49
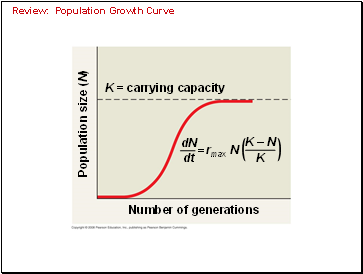
Review: Population Growth Curve
Number of generations
K = carrying capacity
Population size (N)
rmax N
dN
dt
=
K – N
K
Slide 50
You should now be able to:
Define and distinguish between the following sets of terms: density and dispersion; clumped dispersion, uniform dispersion, and random dispersion; life table and reproductive table; Type I, Type II, and Type III survivorship curves; semelparity and iteroparity; r-selected populations and K-selected populations.
Contents
- Population ecology
- Dynamic biological processes influence population density, dispersion, and demographics
- Demographics
- Life history traits are products of natural selection
- Evolution and Life History Diversity
- “Trade-offs” and Life Histories
- The exponential model describes population growth in an idealized, unlimited environment
- Exponential Growth
- The logistic model describes how a population grows more slowly as it nears its carrying capacity
- The Logistic Model and Real Populations
- The Logistic Model and Life Histories
- Many factors that regulate population growth are density dependent
- Population Change and Population Density
- Density-Dependent Population Regulation
- Population Dynamics
- The human population is no longer growing exponentially but is still increasing rapidly
Last added presentations
- Mechanics Lecture
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Sound
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Waves & Sound
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Radiation