Sensory and Motor MechanismsPage
6
6
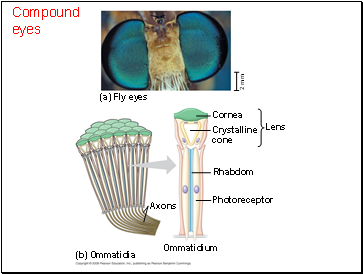
Compound eyes are very effective at detecting movement.
Slide 40
Compound eyes
Rhabdom
(a) Fly eyes
Crystalline cone
Lens
(b) Ommatidia
Ommatidium
Photoreceptor
Axons
Cornea
2 mm
Slide 41
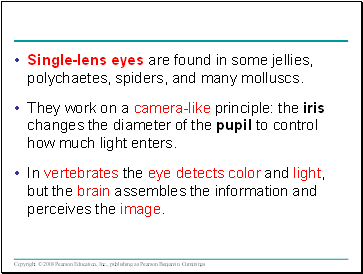
Single-lens eyes are found in some jellies, polychaetes, spiders, and many molluscs.
They work on a camera-like principle: the iris changes the diameter of the pupil to control how much light enters.
In vertebrates the eye detects color and light, but the brain assembles the information and perceives the image.
Slide 42
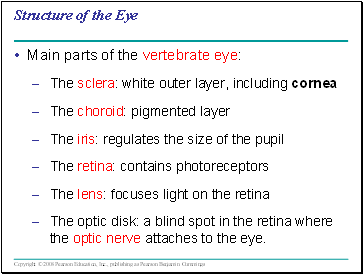
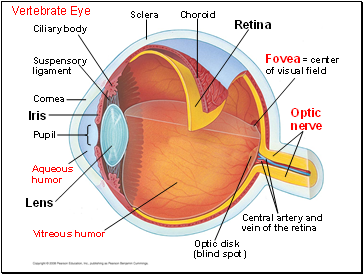
Structure of the Eye
Main parts of the vertebrate eye:
The sclera: white outer layer, including cornea
The choroid: pigmented layer
The iris: regulates the size of the pupil
The retina: contains photoreceptors
The lens: focuses light on the retina
The optic disk: a blind spot in the retina where the optic nerve attaches to the eye.
Slide 43
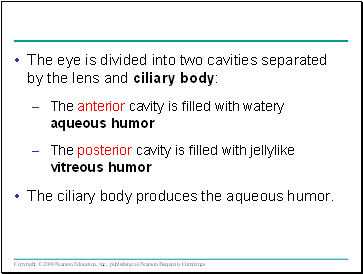
The eye is divided into two cavities separated by the lens and ciliary body:
The anterior cavity is filled with watery aqueous humor
The posterior cavity is filled with jellylike vitreous humor
The ciliary body produces the aqueous humor.
Slide 44
Vertebrate Eye
Optic nerve
Fovea = center of visual field
Lens
Vitreous humor
Optic disk (blind spot)
Central artery and vein of the retina
Iris
Retina
Choroid
Sclera
Ciliary body
Suspensory ligament
Cornea
Pupil
Aqueous humor
Slide 45
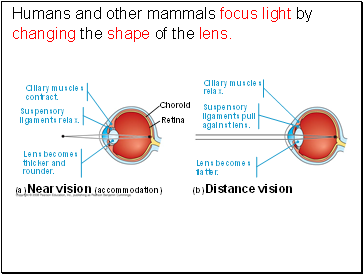
Humans and other mammals focus light by changing the shape of the lens.
Ciliary muscles relax.
Retina
Choroid
(b) Distance vision
(a) Near vision (accommodation)
Suspensory ligaments pull against lens.
Lens becomes flatter.
Lens becomes thicker and rounder.
Ciliary muscles contract.
Suspensory ligaments relax.
Slide 46
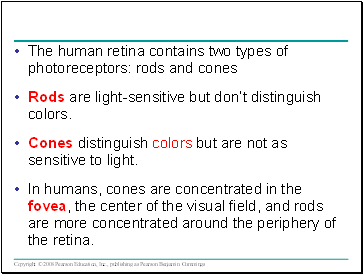
The human retina contains two types of photoreceptors: rods and cones
Rods are light-sensitive but don’t distinguish colors.
Cones distinguish colors but are not as sensitive to light.
In humans, cones are concentrated in the fovea, the center of the visual field, and rods are more concentrated around the periphery of the retina.
Slide 47
Sensory Transduction in the Eye
Contents
- Sensing and Acting
- Sensory Pathways
- Types of Sensory Receptors
- Electromagnetic Receptors
- Thermoreceptors & Pain Receptors
- Sensing Gravity and Sound in Invertebrates
- Hearing and Equilibrium in Mammals
- Hearing
- Equilibrium
- Hearing and Equilibrium in Other Vertebrates
- The senses of taste and smell rely on similar sets of sensory receptors
- Taste in Mammals
- Smell in Humans
- Similar mechanisms underlie vision throughout the animal kingdom
- Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle
- Other Types of Muscle
- Skeletal systems transform muscle contraction into locomotion
- Types of Skeletal Systems
- Types of Locomotion
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Radiation
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Waves & Sound