Plant Structure, Growth, and DevelopmentPage
3
3
Tissue System: Each plant organ has: * dermal * vascular and * ground tissues
Dermal
tissue
Ground
tissue
Vascular
tissue
Slide 21
In nonwoody plants, the dermal tissue system consists of the epidermis.
A waxy coating called the cuticle helps prevent water loss from the epidermis.
In woody plants, protective tissues called periderm replace the epidermis in older regions of stems and roots.
Trichomes are outgrowths of the shoot epidermis and can help with insect defense.
Slide 22
The vascular tissue system carries out long-distance transport of materials between roots and shoots.
Xylem conveys water and dissolved minerals upward from roots into the shoots.
Phloem transports organic nutrients from where they are made to where they are needed.
Slide 23
Tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular are the ground tissue system.
Ground tissue internal to the vascular tissue is pith; ground tissue external to the vascular tissue is cortex. Both have plastids for storage.
Ground tissue includes cells specialized for storage, photosynthesis, and support.
Slide 24
Common Types of Plant Cells - are specialized of cells in structure and function.
Some major types of plant cells:
Parenchyma - ground: thin flexible cell walls: photosynthesis, storage.
Collenchyma - ground: thicker cell walls for flexible support.
Sclerenchyma - ground: thick secondary cell walls reinforced with lignin for rigid, sturdy support.
Xylem - vascular: water-conducting cells.
Phloem - vascular: sugar-conducting cells.
Slide 25
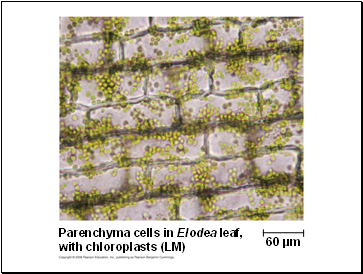
Parenchyma cells in Elodea leaf,
with chloroplasts (LM)
60 µm
Slide 26
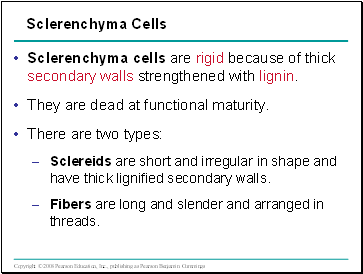
Sclerenchyma Cells
Sclerenchyma cells are rigid because of thick secondary walls strengthened with lignin.
They are dead at functional maturity.
There are two types:
Sclereids are short and irregular in shape and have thick lignified secondary walls.
Fibers are long and slender and arranged in threads.
Slide 27
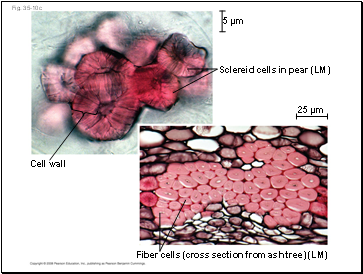
Fig. 35-10c
5 µm
25 µm
Sclereid cells in pear (LM)
Fiber cells (cross section from ash tree) (LM)
Cell wall
Slide 28
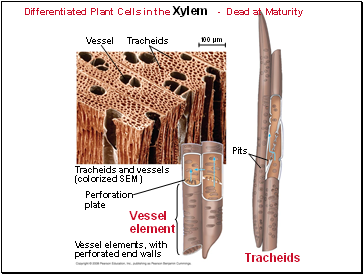
Differentiated Plant Cells in the Xylem - Dead at Maturity
Perforation
Contents
- Plastic Plants?
- The Three Basic Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves
- Common Types of Plant Cells - are specialized of cells in structure and function.
- Primary Growth - Lengthens Roots and Shoots
- Primary Growth of Shoots - Apical Meristems
- The Vascular Cambium and Secondary Vascular Tissue
- The Cork Cambium and the Production of Periderm
- Growth: Cell Division and Cell Expansion
- Morphogenesis and Pattern Formation
- Gene Expression and Control of Cellular Differentiation
- Location and a Cell’s Developmental Fate
- Genetic Control of Flowering
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Upcoming Classes
- Space Radiation
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation