Animal BehaviorPage
9
9
Slide 67
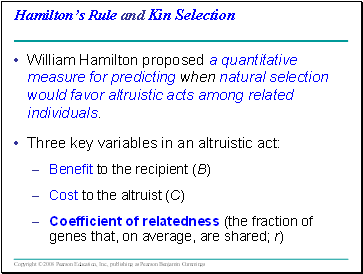
Hamiltonís Rule and Kin Selection
William Hamilton proposed a quantitative measure for predicting when natural selection would favor altruistic acts among related individuals.
Three key variables in an altruistic act:
Benefit to the recipient (B)
Cost to the altruist (C)
Coefficient of relatedness (the fraction of genes that, on average, are shared; r)
Slide 68
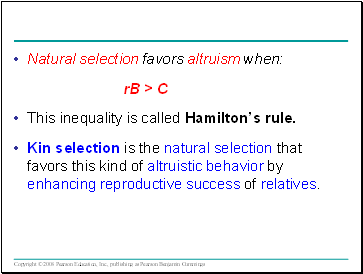
Natural selection favors altruism when:
rB > C
This inequality is called Hamiltonís rule.
Kin selection is the natural selection that favors this kind of altruistic behavior by enhancing reproductive success of relatives.
Slide 69
Reciprocal Altruism
Altruistic behavior toward unrelated individuals can be adaptive if the aided individual returns the favor in the future. This type of altruism is called reciprocal altruism.
Reciprocal altruism is limited to species with stable social groups where individuals meet repeatedly, and cheaters (donít reciprocate) are punished. Reciprocal altruism has been used to explain altruism between unrelated individuals in humans.
Slide 70
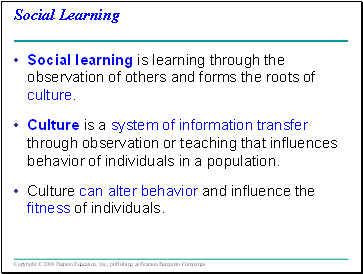
Social Learning
Social learning is learning through the observation of others and forms the roots of culture.
Culture is a system of information transfer through observation or teaching that influences behavior of individuals in a population.
Culture can alter behavior and influence the fitness of individuals.
Slide 71
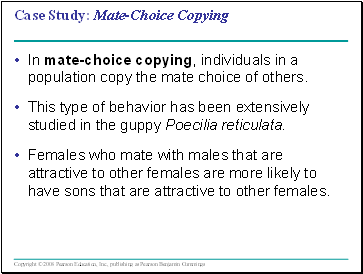
Case Study: Mate-Choice Copying
In mate-choice copying, individuals in a population copy the mate choice of others.
This type of behavior has been extensively studied in the guppy Poecilia reticulata.
Females who mate with males that are attractive to other females are more likely to have sons that are attractive to other females.
Slide 72
Case Study: Social Learning of Alarm Calls
Vervet monkeys produce distinct alarm calls for different predators.
Infant monkeys give undiscriminating calls but learn to fine-tune them by the time they are adults.
Slide 73
Vervet monkeys learning correct use of alarm calls
Slide 74
Evolution and Human Culture
No other species comes close to matching the social learning and cultural transmission that occurs among humans.
Contents
- Shall We Dance?
- Fixed Action Patterns FAP
- Migration
- Behavioral Rhyths
- Animal Signals and Communication
- Pheromones
- Habituation
- Imprinting
- Spatial Learning
- Associative Learning
- Cognition and Problem Solving
- Genetically Based Behavioral Variation in Natural Populations
- Mating Behavior and Mate Choice
- Evolution and Human Culture
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Space Radiation
- Newtonís laws of motion
- Friction
- Waves & Sound
- Static and Kinetic Friction