RadiationPage
4
4
Absorbed Dose: rad (Roentgen absorbed dose) = absorption of 100 ergs of energy from any radiation in 1 gram of any material; 1 Gray (Gy) = 100 rads = 1 Joule/kg; Exposure to 1 Roentgen approximates 0.9 rad in air.
Biologically Equivalent Dose: Rem (Roentgen equivalent man) = dose in rads x QF, where QF = quality factor. 1 Sievert (Sv) = 100 rems.
Slide 37
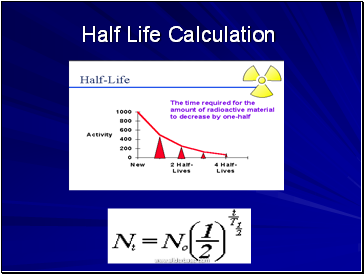
Half Life Calculation
Slide 38
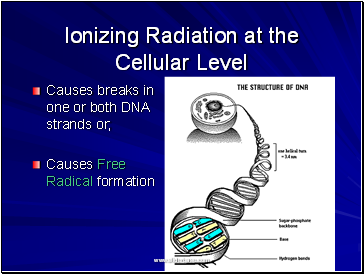
Ionizing Radiation at the Cellular Level
Causes breaks in one or both DNA strands or;
Causes Free Radical formation
Slide 39
Exposure Limits
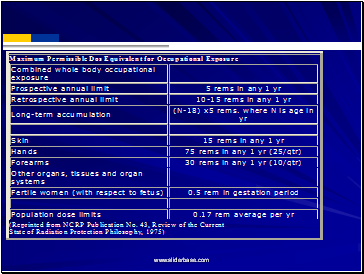
OSHA Limits: Whole body limit = 1.25 rem/qtr or 5 rem (50 mSv) per year.
Hands and feet limit = 18.75 rem/qtr.
Skin of whole body limit = 7.5 rem/qtr.
Total life accumulation = 5 x (N-18) rem where N = age. Can have 3 rem/qtr if total life accumulation not exceeded.
Note: New recommendations reduce the 5 rem to 2 rem.
Slide 40
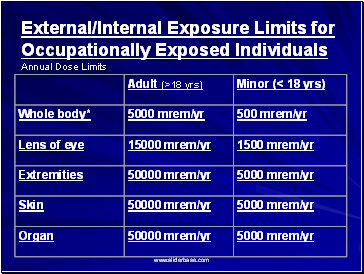
External/Internal Exposure Limits for Occupationally Exposed Individuals
Annual Dose Limits
*Effective dose equivalent
Slide 41
Slide 42
Community Emergency Radiation
Hazardous Waste Sites:
Radiation above background (0.01-0.02 m rem/hr) signifies possible presence which must be monitored. Radiation above 2 m rem/hr indicates potential hazard. Evacuate site until controlled.
Slide 43
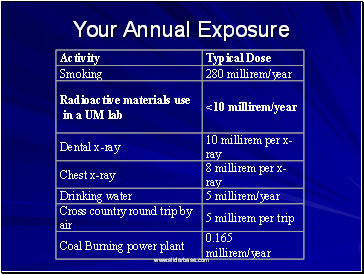
Your Annual Exposure
Slide 44
HEALTH EFFECTS
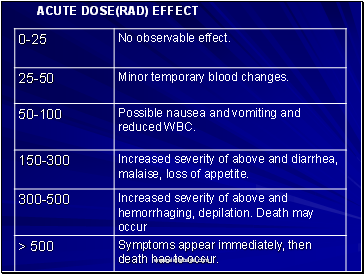
Generalizations: Biological effects are due to the ionization process that destroys the capacity for cell reproduction or division or causes cell mutation. A given total dose will cause more damage if received in a shorter time period. A fatal dose is (600 R)
Acute Somatic Effects: Relatively immediate effects to a person acutely exposed. Severity depends on dose. Death usually results from damage to bone marrow or intestinal wall. Acute radio-dermatitis is common in radiotherapy; chronic cases occur mostly in industry.
Slide 45
ACUTE DOSE(RAD) EFFECT
Slide 46
Delayed Somatic Effects: Delayed effects to exposed person include: Cancer, leukemia, cataracts, life shortening from organ failure, and abortion. Probability of an effect is proportional to dose (no threshold). Severity is independent of dose. Doubling dose for cancer is approximately 10-100 rems.
Contents
- Definition of Radiation
- Radioactivity: Elements & Atoms
- Radioactivity
- Ionization
- Types of Radiation
- Ionizing Versus Non-ionizing Radiation
- Ionizing Radiation
- Another Definition
- Beta Particles
- Gamma Rays
- X-Rays
- Neutrons
- Exposure Limits
- Community Emergency Radiation
- Non-ionizing Radiation
- Effects
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Health Physics
- Sound
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions