Hormones and the Endocrine SystemPage
11
11
Slide 72
The testes primarily synthesize androgens, mainly testosterone, which stimulate development and maintenance of the male reproductive system and male secondary sex characteristics.
Testosterone causes an increase in muscle and bone mass and is often taken as a supplement to cause muscle growth, which carries health risks.
Slide 73
Estrogens, made in the ovary, most importantly estradiol, are responsible for maintenance of the female reproductive system and the development of female secondary sex characteristics.
In mammals, progestins, which include progesterone, are primarily involved in preparing and maintaining the uterus.
Synthesis of the sex hormones is controlled by FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary.
Slide 74
Pineal Gland - Melatonin and Biorhyths
The pineal gland, located in the brain, secretes melatonin.
Light/dark cycles control release of melatonin.
Primary functions of melatonin appear to relate to biological rhyths associated with reproduction.
Slide 75
Signal Transduction Pathway
Example
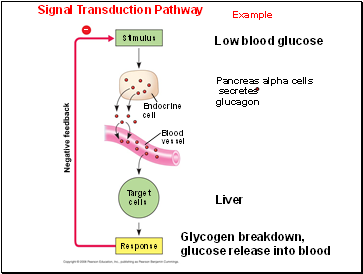
Stimulus
Low blood glucose
Pancreas alpha cells
secretes glucagon
Endocrine
cell
Blood
vessel
Liver
Target
cells
Response
Glycogen breakdown, glucose release into blood
Negative feedback
–
Slide 76
You should now be able to:
Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: hormones and local regulators, paracrine and autocrine signals.
Describe the evidence that steroid hormones have intracellular receptors, while water-soluble hormones have cell-surface receptors.
Explain how the antagonistic hormones insulin and glucagon regulate carbohydrate metabolism.
Distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Slide 77
Explain how the hypothalamus and the pituitary glands interact and how they coordinate the endocrine system.
Explain the role of tropic hormones in coordinating endocrine signaling throughout the body.
List and describe the functions of hormones released by the following: anterior and posterior pituitary lobes, thyroid glands, parathyroid glands, adrenal medulla, adrenal cortex, gonads, pineal gland.
Contents
- The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators
- Types of Secreted Signaling Molecules
- Local Regulators = Short Distance Chemical Signals
- Neurotransmitters and Neurohormones
- Pheromones
- Chemical Classes of Hormones
- Cellular Response Pathways
- Pathway for Water-Soluble Hormones
- Pathway for Lipid-Soluble Hormones
- Multiple Effects of Hormones
- Signaling by Local Regulators
- Simple Hormone Pathways
- Insulin and Glucagon: Control of Blood Glucose
- Target Tissues for Insulin and Glucagon
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Posterior Pituitary Hormones
- Anterior Pituitary Hormones
- Hormone Cascade Pathways
- Tropic Hormones
- Nontropic Hormones - target nonendocrine tissues.
- Growth Hormone
- Thyroid Hormone: Control of Metabolism and Development
- Parathyroid Hormone and Vitamin D: Control of Blood Calcium
- Adrenal Hormones: Response to Stress
- Catecholamines from the Adrenal Medulla
- Steroid Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex
- Gonadal Sex Hormones
- Pineal Gland - Melatonin and Biorhyths
Last added presentations
- Space Radiation
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Thermal Energy
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Friction