Atomic Structure and Periodic TrendsPage
2
2
Consider 3 approaches:
Classical
Bohr Model (old quantum theory)
Full Quantum: Schrödinger Equation
Slide 10
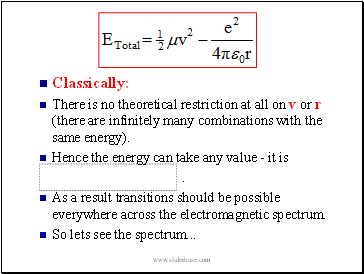
Classically:
There is no theoretical restriction at all on v or r (there are infinitely many combinations with the same energy).
Hence the energy can take any value - it is
.
As a result transitions should be possible everywhere across the electromagnetic spectrum.
So lets see the spectrum .
Slide 11
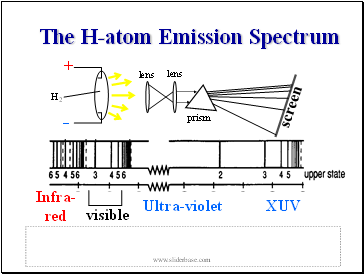
The H-atom Emission Spectrum
Slide 12
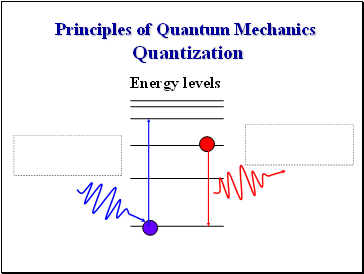
Principles of Quantum Mechanics Quantization
Energy levels
Slide 13
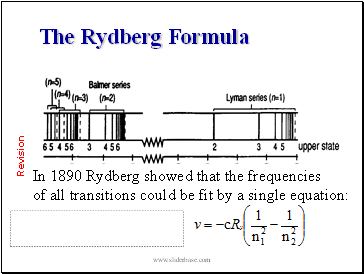
The Rydberg Formula
In 1890 Rydberg showed that the frequencies
of all transitions could be fit by a single equation:
Revision
Slide 14
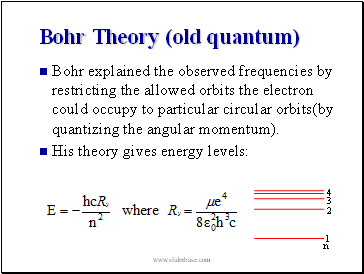
Bohr Theory (old quantum)
Bohr explained the observed frequencies by restricting the allowed orbits the electron could occupy to particular circular orbits(by quantizing the angular momentum).
His theory gives energy levels:
Slide 15
The problem with Bohr Theory
Bohr theory works extremely well for the H-atom.
However;
it provides no explanation for the quantization of energy -it just happens to fit the observed spectrum
But, more seriously:
it just doesnít work at all for any other atoms
Slide 16
Quantum mechanical Principles and the Solution of the Schrödinger Equation
Slide 17
Principles of Quantum Mechanics Quantization
Energy levels
Quantum mechanics
Classical mechanics
is continuous
Slide 18
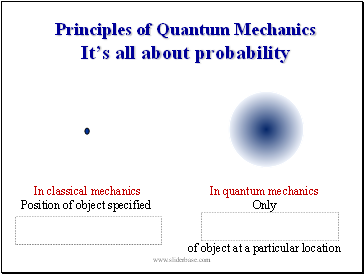
Principles of Quantum Mechanics Itís all about probability
In classical mechanics
Position of object specified
In quantum mechanics
Only
of object at a particular location
Slide 19
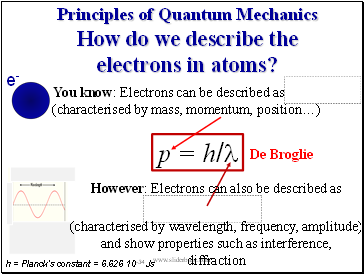
Principles of Quantum Mechanics How do we describe the electrons in atoms?
You know: Electrons can be described as
(characterised by mass, momentum, positionÖ)
p = h/l
De Broglie
e-
h = Planckís constant = 6.626 10-34 Js
However: Electrons can also be described as
(characterised by wavelength, frequency, amplitude)
Contents
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Trends
- Why study atomic electronic structure?
- The Periodic Table
- The Hydrogen Atom
- Energy Levels?
- The Rydberg Formula
- Bohr Theory (old quantum)
- The problem with Bohr Theory
- Quantum mechanical Principles and the Solution of the Schrödinger Equation
- The Results of Quantum Mechanics
- Spherical Polar Coordinates
- The quantum numbers;
- The Radial Wavefunctions
- Revisit: The Born Interpretation
- Radial Wavefunctions and the Born Interpretation
- The Surface area of a sphere is hence:
- Construction of the radial distribution function
- Radial distribution function P(r)
- The Angular Wavefunction
- The Shapes of Wavefunctions (Orbitals)
- Electron densities representations
- The energies of orbitals
- The Ionization Energy
- Other Atoms
- Periodic Trends
- Space for extra Notes
- More on Ionization Energies
- More Periodic Trends
- Appendices
Last added presentations
- Space Radiation
- Waves & Sound
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Friction
- Health Physics
- Newtonís Laws of Motion
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy