ChromosomePage
12
12
The existence of inversion was first detected by Strutevant and Plunkett in 1926.
Inversion occur when parts of chromosomes become detached , turn through 1800 and are reinserted in such a way that the genes are in reversed order.
For example, a certain segment may be broken in two places, and the breaks may be in close proximity because of chance loop in the chromosome.
When they rejoin, the wrong ends may become connected.
The part on one side of the loop connects with broken end different from the one with which it was formerly connected.
This leaves the other two broken ends to become attached.
The part within the loop thus becomes turned around or inverted.
Slide 76
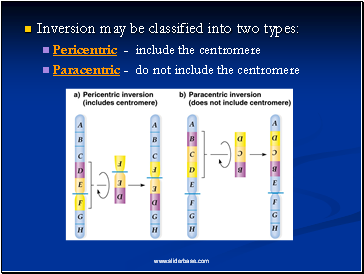
Inversion may be classified into two types:
Pericentric - include the centromere
Paracentric - do not include the centromere
Slide 77
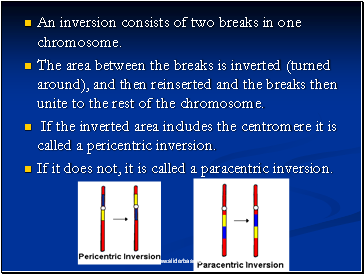
An inversion consists of two breaks in one chromosome.
The area between the breaks is inverted (turned around), and then reinserted and the breaks then unite to the rest of the chromosome.
If the inverted area includes the centromere it is called a pericentric inversion.
If it does not, it is called a paracentric inversion.
Slide 78
Inversions in natural populations
In natural populations, pericentric inversions are much less frequent than paracentric inversions.
In many sp, however, pericentric inversions are relatively common, e.g., in some grasshoppers.
Paracentric inversions appear to be very frequent in natural populations of Drosophila.
Slide 79
Translocation
Integration of a chromosome segment into a nonhomologous chromosome is known as translocation.
Three types:
1. simple translocation
2. shift
3. reciprocal translocation.
Slide 80
Simple translocation: In this case, terminal segment of a chromosome is integrated at one end of a non-homologous region. Simple translocations are rather rare.
Shift: In shift, an intercalary segment of a chromosome is integrated within a non-homologous chromosome. Such translocations are known in the populations of Drosophila, Neurospora etc.
Reciprocal translocation: It is produced when two non-homologous chromosomes exchange segments – i.e., segments reciprocally transferred.
Translocation of this type is most common
Slide 81
Non-Disjunction
Generally during gametogenesis the homologous chromosomes of each pair separate out (disjunction) and are equally distributed in the daughter cells.
Contents
- What Exactly is a chromosome?
- Number of chromosomes
- Chromosome Size
- Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
- Satellite DNAs
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
- Prokaryotic chromosome
- Bacterial Chromosome
- Supercoiling
- Mechanism of folding of a bacterial chromosome
- Chromatin
- Centromeres and Telomeres
- Centromere
- Kinetochore
- Telomere
- Telomere Repeat Sequences
- Staining and Banding chromosome
- Chromosomal Aberrations
- Structural Chromosomal Aberrations
- Deletion or deficiency
- Deletion in Prokaryotes
- Duplication
- Origin
- Inversion
- Inversions in natural populations
- Translocation
- Non-Disjunction
- Variation in chromosome number
- More about Aneuploidy
- Uses of Aneuploidy
- Trisomy in Humans
- Amniocentesis for Detecting Aneuploidy
- Other Syndromes
- Giant chromosomes
- Lampbrush Chromosome
- Dosage Compensation
- Barr Bodies
- Mechanism of X-chromosome Inactivation
- Reading assignment
Last added presentations
- Health Physics
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Gravitation