ChromosomePage
5
5
The folded nature of chromosome is due to the incorporation of RNA with DNA.
There are about 50 loops in the chromosome of E.coli.
These loops are highly twisted or supercoiled structure with about four million nucleotide pairs.
Its molecular weight is about 2.8 X109
During replication of DNA, the coiling must be relaxed.
DNA gyrase is necessary for the unwinding the coils.
Slide 28
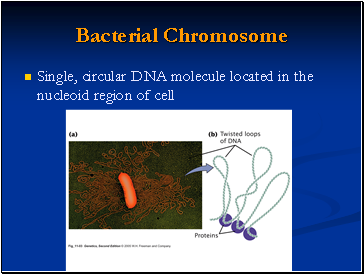
Bacterial Chromosome
Single, circular DNA molecule located in the nucleoid region of cell
Slide 29
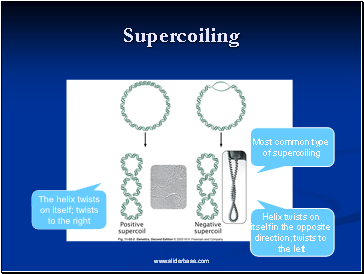
Supercoiling
Slide 30
Supercoiling
The helix twists on itself; twists to the right
Helix twists on
itself in the opposite
direction; twists to
the left
Most common type
of supercoiling
Slide 31
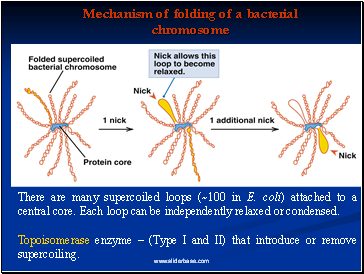
Mechanism of folding of a bacterial chromosome
There are many supercoiled loops (~100 in E. coli) attached to a central core. Each loop can be independently relaxed or condensed.
Topoisomerase enzyme – (Type I and II) that introduce or remove supercoiling.
Slide 32
Chromatin
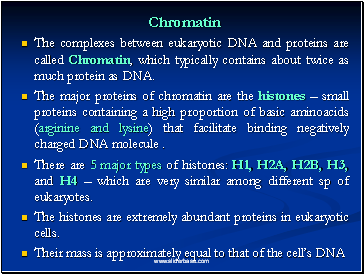
The complexes between eukaryotic DNA and proteins are called Chromatin, which typically contains about twice as much protein as DNA.
The major proteins of chromatin are the histones – small proteins containing a high proportion of basic aminoacids (arginine and lysine) that facilitate binding negatively charged DNA molecule .
There are 5 major types of histones: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 – which are very similar among different sp of eukaryotes.
The histones are extremely abundant proteins in eukaryotic cells.
Their mass is approximately equal to that of the cell’s DNA
Slide 33
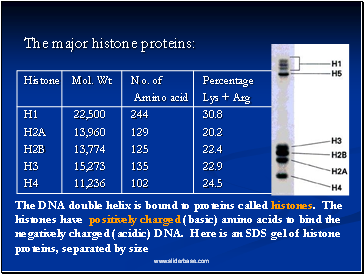
The major histone proteins:
Histone Mol. Wt No. of Percentage
Amino acid Lys + Arg
H1 22,500 244 30.8
H2A 13,960 129 20.2
H2B 13,774 125 22.4
H3 15,273 135 22.9
H4 11,236 102 24.5
The DNA double helix is bound to proteins called histones. The histones have positively charged (basic) amino acids to bind the negatively charged (acidic) DNA. Here is an SDS gel of histone proteins, separated by size
Slide 34
In addition, chromatin contains an approximately equal mass of a wide variety of non-histone chromosomal proteins.
There are more than a thousand different types of these proteins, which are involved in a range of activities, including DNA replication and gene expression.
Contents
- What Exactly is a chromosome?
- Number of chromosomes
- Chromosome Size
- Euchromatin and Heterochromatin
- Satellite DNAs
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosomes
- Prokaryotic chromosome
- Bacterial Chromosome
- Supercoiling
- Mechanism of folding of a bacterial chromosome
- Chromatin
- Centromeres and Telomeres
- Centromere
- Kinetochore
- Telomere
- Telomere Repeat Sequences
- Staining and Banding chromosome
- Chromosomal Aberrations
- Structural Chromosomal Aberrations
- Deletion or deficiency
- Deletion in Prokaryotes
- Duplication
- Origin
- Inversion
- Inversions in natural populations
- Translocation
- Non-Disjunction
- Variation in chromosome number
- More about Aneuploidy
- Uses of Aneuploidy
- Trisomy in Humans
- Amniocentesis for Detecting Aneuploidy
- Other Syndromes
- Giant chromosomes
- Lampbrush Chromosome
- Dosage Compensation
- Barr Bodies
- Mechanism of X-chromosome Inactivation
- Reading assignment
Last added presentations
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Health Physics
- Radiation
- Gravitation
- Space Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort